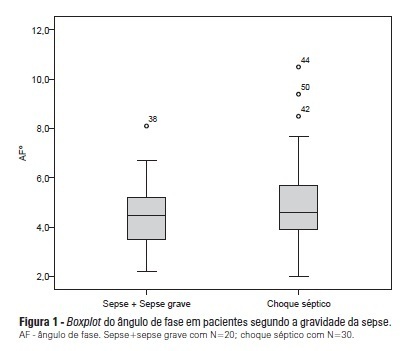
OBJECTIVE: To calculate the values of the phase angle of septic patients using bioelectrical impedance analysis, correlate the values with clinical and biochemical variables, and compare them to reference values. METHODS: Cohort study conducted with 50 septic patients aged ≥18 years old, admitted to intensive care units, and assessed according to prognostic indexes (APACHE II and SOFA), clinical progression (mortality, severity of sepsis, length of stay in intensive care unit), biochemical parameters (albumin and C-reactive protein), and the phase angle. RESULTS: The average age of the sample was 65.6±16.5 years. Most patients were male (58%) and suffering from septic shock (60%). The average APACHE II and SOFA scores were 22.98±7.1 and 7.5±3.4, respectively. The patients who survived stayed nine days on average (five to 13) in the intensive care unit, and the mortality rate was 30%. The average value of the phase angle was 5.4±2.6° in the total sample and was smaller among the females compared with the males (p=0.01). The phase angle measures did not exhibit an association with the severity of the sepsis, mortality, gender, and age or correlate with the length of hospitalization or the biochemical parameters. The participants’ phase angle values adjusted per gender and age were 1.1 to 1.9 times lower compared with the values for a normal population. CONCLUSION: The average value of the phase angle of septic patients was lower compared with the reference values for a healthy population. The phase angle measures did not exhibit association with the clinical and biochemical variables, which might be explained by the sample homogeneity.
Search
Search in:


Comments