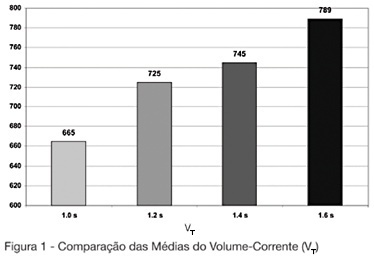
BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: The mechanical ventilator support is one of the main used modalities of support in intensive therapy. In the modality of predetermined pressure, the maximum pressure is regulated, but the current volume (V T) is a complex function of the applied pressure and its speed to reach the pressure-target, of the available breathing time and the resistance to the breath. This paper has as objective to evaluate the influences of the increment of the breathing time in the pulmonary ventilation. METHODS: The study was carried through in the Adult ICU of the Regional Hospital of Mato Grosso do Sul, located in Campo Grande. They had been enclosed individuals adult, both genders, between 16 and 84 years, submitted to the mechanical ventilation in controlled pressure mode or in controlled-watched mode. The breathing time was adjusted in 1 sec, developing in 0.2 sec until the boundary-value of 1.6 sec. The tidal volume (V T) and the volume minute (V E) had been evaluated of 13 patients in the breathing times of 1s; 1.2s; 1.4s and 1.6s. RESULTS: In the mean of V T and V E an increasing increase was observed after-increment of the breathing time. We did not find in consulted literature, data which correlated the breathing time with alterations in the current volume. CONCLUSIONS: The increment of the breathing time in the ventilation for pressure control can have influence in the determination of the current volume offered to the patient.
Search
Search in:


Comments