To investigate the association between the rapid shallow breathing index and successful extubation in patients with traumatic brain injury.
This study was a prospective study conducted in patients with traumatic brain injury of both genders who underwent mechanical ventilation for at least two days and who passed a spontaneous breathing trial. The minute volume and respiratory rate were measured using a ventilometer, and the data were used to calculate the rapid shallow breathing index (respiratory rate/tidal volume). The dependent variable was the extubation outcome: reintubation after up to 48 hours (extubation failure) or not (extubation success). The independent variable was the rapid shallow breathing index measured after a successful spontaneous breathing trial.
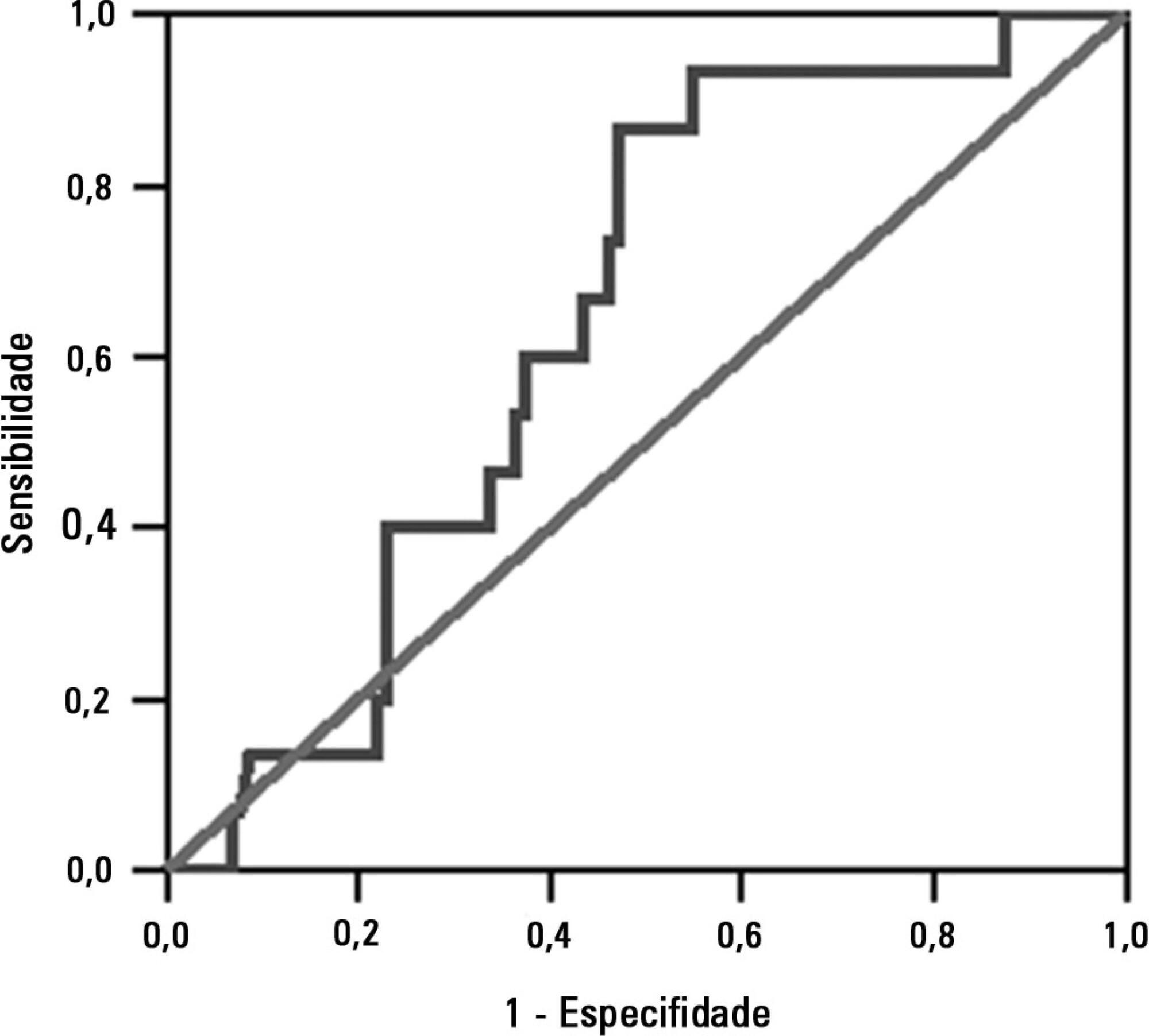
The sample comprised 119 individuals, including 111 (93.3%) males. The average age of the sample was 35.0±12.9 years old. The average duration of mechanical ventilation was 8.1±3.6 days. A total of 104 (87.4%) participants achieved successful extubation. No association was found between the rapid shallow breathing index and extubation success.
The rapid shallow breathing index was not associated with successful extubation in patients with traumatic brain injury.
Search
Search in:


Comments