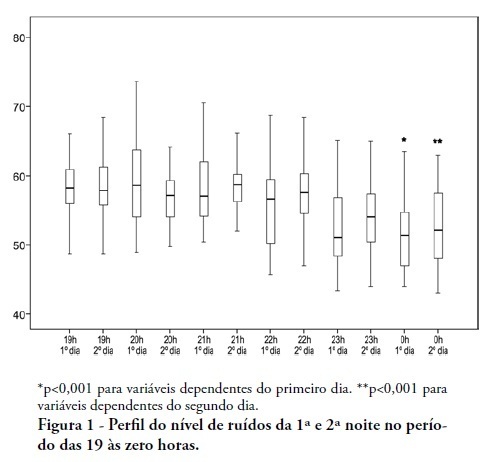
OBJECTIVES: To identify the main causes of stress in patients staying in a coronary unit and to assess the influence of noise levels on their perception of stress. METHODS: This was a prospective, descriptive and quantitative study conducted between June and November 2009 in the Coronary Unit of the Hospital de Clínicas da Universidade Estadual de Campinas. The Intensive Care Unit Environmental Stressor Scale was used on the first, second and third days of hospitalization to identify stressors. The noise level was measured on the first and second nights using an Instrutherm DEC-460 decibel meter. RESULTS: Overall, 32 clinical heart disease patients were included. The median Intensive Care Unit Environmental Stressor Scale scores were 67.5, 60.5 and 59.5 for the first, second and third days, respectively. The differences were not statistically significant. The highest noise level (a median of 58.7 dB) was detected on the second night at 9:00 pm; the lowest level (51.5 dB) was measured on the first night at 12:00 am. In a multiple linear regression model, the first-night noise level had a 33% correlation with the second-day stress scale score, and for the second night, the correlation with the third-day stress scale score was 32.8% (p = 0.001). CONCLUSION: Patients admitted into a coronary unit have an increased perception of stress. Higher noise levels are also responsible for the perception of stress in these patients.
Search
Search in:


Comments