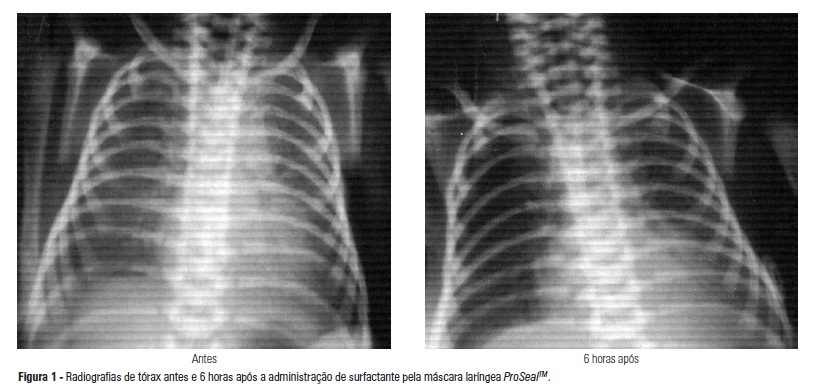
The administration of surfactant via tracheal cannula with mechanical ventilation is the conventional treatment for infant respiratory distress syndrome. Hemodynamic and respiratory changes due to tracheal intubation and the need for premedication justify the search for less invasive alternatives of surfactant administration. The objective of this study was to describe the use of the ProSealTM laryngeal mask airway as an option for the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome in a premature infant born at 31 weeks of gestation, at 1335 g, with respiratory difficulty after the first hour of life and exhibiting the clinical and radiologic features of respiratory distress syndrome. The surfactant was administered with the use of the ProSealTM laryngeal mask airway at 3.5 hours of life. It was well tolerated, with no need for tracheal intubation. Normal gasometry and radiologic improvement were observed after three and six hours of administration. Oxygen administration was suspended after eight days, with no comorbidities at discharge. The laryngeal mask airway seems to be a painless and less invasive alternative to treat respiratory distress syndrome and may reduce the need for tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation. The efficacy and advantages of this route of treatment should be confirmed in a study of an adequate sample.
Search
Search in:


Comments