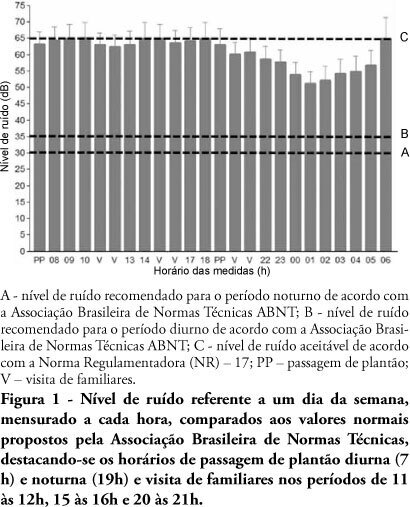
OBJECTIVE: The several multidisciplinary team personnel and device alarms make intensive care units noisy environments. This study aimed to measure the noise level of a medical-surgical intensive care unit in Recife, Brazil, and to assess the noise perception by the unit’s healthcare professionals. METHODS: A decibel meter was used for continuous every five seconds one week noise levels recording. After this measurement, an interview shaped noise perception questionnaire was applied to the healthcare professionals, approaching the discomfort level and noise control possibilities. RESULTS: Mean 58.21 ± 5.93 dB noise was recorded. The morning noise level was higher than at night (60.85 ± 4.90 versus 55.60 ± 5.98, p <0.001), as well as work-days versus weekend (58. 77 ± 6.05 versus 56.83 ± 5.90, p <0.001). The evening staff shift change noise was louder than by daytime change (62.31 ± 4.70 versus 61.35 ± 5.08 dB; p < 0.001). Of the 73 questionnaire respondents, 97.3% believe that the intensive care unit has moderate or intense noise levels; 50.7% consider the noise harmful; and 98.6% believe that noise levels can be reduced. CONCLUSION: The measured noise levels were above the recommended. Preventive and educational programs approaching the importance of noise levels reduction should be encouraged in intensive care units.
Search
Search in:


Comments